Previous Tutorial: Reading an Imported Mesh in Unity
Intro
In this tutorial we'll be using the project created in the previous tutorial: Reading an Imported Mesh in Unity, and we'll be using concepts and code covered in the previous guides.
In this guide we will cover:
- Using a Unity Node Visualizer for displaying the graph
The majority of this tutorial is specific to Unity. It provides some helper functions to easily place (and fast rendering) points in space related to the DHART output.
Node Visualizer
The main component of this tutorial is using a node visualization script. As this is Unity specific, we won't go into detail explaining the script. It has an extra feature for coloring nodes which we don't take advantage of, but could easily be used for coloring nodes by a score or weight.
First, create a script called NodeVisualizer.cs.
Copy and paste the following code into this file.
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
namespace DHARTUTILS
{
public enum NodeScoreType {
edgeConnection,
linear
};
[RequireComponent(typeof(ParticleSystem))]
public class NodeVisualizer : MonoBehaviour
{
public ParticleSystem nodeParticleSystem;
public static NodeVisualizer instance;
void Awake()
{
instance = this;
nodeParticleSystem = GetComponent<ParticleSystem>();
}
public void VisualizeAllToAllNode(
Vector3D position, Color color)
{
ParticleSystem.MainModule psMain = nodeParticleSystem.main;
psMain.startColor = color;
nodeParticleSystem.transform.position =
new Vector3(position.
x, position.
y, position.
z);
nodeParticleSystem.Emit(1);
}
public List<Color> CreateColors(float[] scores)
{
GradientColorKey[] gradientColorKeys = new GradientColorKey[3];
gradientColorKeys[0].color = Color.red;
gradientColorKeys[0].time = 0.0f;
gradientColorKeys[1].color = Color.green;
gradientColorKeys[1].time = 0.5f;
gradientColorKeys[2].color = Color.blue;
gradientColorKeys[2].time = 1.0f;
GradientAlphaKey[] gradientAlphaKeys = new GradientAlphaKey[3];
gradientAlphaKeys[0].alpha = 1.0f;
gradientAlphaKeys[0].time = 0.0f;
gradientAlphaKeys[1].alpha = 1.0f;
gradientAlphaKeys[1].time = 1.0f;
gradientAlphaKeys[2].alpha = 1.0f;
gradientAlphaKeys[2].time = 1.0f;
Gradient gradient = new Gradient();
gradient.colorKeys = gradientColorKeys;
gradient.alphaKeys = gradientAlphaKeys;
float maxScore = 0.0f;
for (int i = 0; i < scores.Length; i++)
{
float currScore = scores[i];
if (currScore > maxScore)
maxScore = currScore;
}
float[] clampedScores = new float[scores.Length];
List<Color> colors = new List<Color>();
for (int i = 0; i < scores.Length; i++)
{
float value = scores[i];
if (float.IsInfinity(value) || float.IsNaN(value))
{
Debug.Log("Aggregated edge cost result equaled infinity or NaN." +
"Setting its value in the array to 0 to avoid crashes.");
continue;
}
clampedScores[i] = Mathf.Clamp(scores[i], 0, maxScore) / maxScore;
Color color = gradient.Evaluate(clampedScores[i]);
colors.Add(color);
}
return colors;
}
}
}
Automated analysis of the built environent
Definition: CommonTypes.cs:9
A three dimensional vector with built in utility functions.
Definition: CommonTypes.cs:40
readonly float y
Y component of this vector.
Definition: CommonTypes.cs:42
readonly float x
X component of this vector.
Definition: CommonTypes.cs:41
readonly float z
Z component of this vector.
Definition: CommonTypes.cs:43
Setting the Particle Property
First we will make a new material that will be used by the particle system. Navigate (or create) a folder in the Assets called Materials.
Right click and Create->Material

Rename the material to "Node Material" and select it in the Assets browser.
In the Inspector, match the values shown in the following image. Specifically, the Shader dropdown should be set to UI->Default.
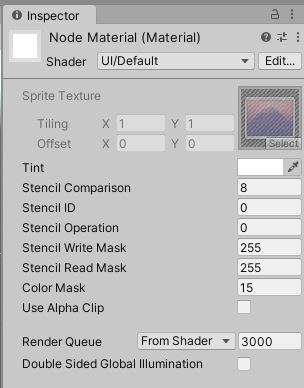
Material Properties
- Make an empty game object in the scene hierarchy called "NodeViz".
- Drag and drop the
NodeVisualization.cs script onto the NodeViz game object.
Particle System
Now that there is a particle system, go through each setting and make sure it matches the settings shown in the images below. Note that the Renderer has a material, which is what you will use to assign the material created in the step above.
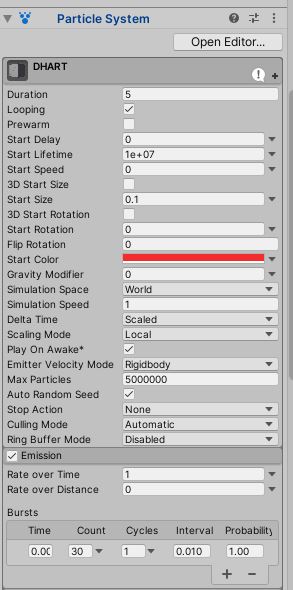
Particle System
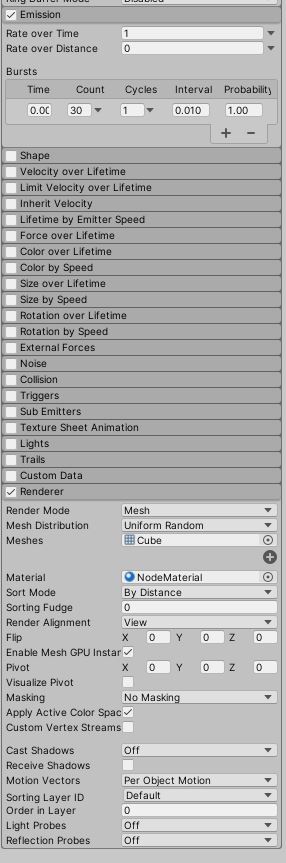
Particle System
Generating a Graph
At this point we assume you have followed the previous tutorials, and so much of this code should be easy enough to follow along. If you have any questions please post on the github Discussions page.
- Create a script called
DHART_Graph.cs
Drag this script onto the Main Camera game object
This script is largely a combination of the previous tutorials with a few differences.
- We take a gameobject for a starting point that can be used to interactively change where the graph starts.
- The graph nodes are copied to C# and the coordinates are converted back to Unity.
- The converted nodes are visualized by passing to a function we call
PlotNodes().
using UnityEngine;
using System.Linq;
using DHARTUTILS;
public class DHART_Graph : MonoBehaviour
{
public int max_nodes = 100;
public GameObject StartPoint;
public Node[] nodes =
null;
public GameObject MeshParent;
private NodeVisualizer nodeVisualizer;
void Start()
{
nodeVisualizer = NodeVisualizer.instance;
MeshParent.SetActive(true);
var meshes = MeshUtils.GetMeshesFromParent(MeshParent);
this.CreateSeperateBVH(meshes);
Vector3 start_point = this.StartPoint.transform.position;
start_point = new Vector3(start_point.x * -1, start_point.z * -1, start_point.y);
this.CreateGraph(start_point);
Vector3[] nodes_vec = TransformUtils.Node_to_Vector(graph_nodes);
Vector3[] nodes_Yup = TransformUtils.PointList_Z2Y(nodes_vec);
Vector3[] nodes_Lcoor = TransformUtils.PointList_R2L(nodes_Yup);
PlotNodes(nodes_Lcoor, 0, 0, 1);
}
public void CreateSeperateBVH(Mesh[] global)
{
for (int i = 0; i < Meshes.Length; i++)
{
var tris = global[i].triangles;
var vert_array = MeshUtils.FlattenVerticeArray(global[i].vertices, true);
var mesh_name = global[i].
name;
if(vert_array.Length > 0){
Meshes[i] =
new MeshInfo(tris, vert_array, mesh_name);
}
}
Meshes = Meshes.Where(c => c != null).ToArray();
MeshInfo[] Doors = Meshes.Where(mesh => (mesh.name.ToLower().Contains(
"door"))).ToArray();
MeshInfo[] Windows = Meshes.Where(mesh => (mesh.name.ToLower().Contains(
"window"))).ToArray();
MeshInfo[] Global = Meshes.Except(Doors).Except(Windows).ToArray();
var walkableMesh = Global.Union(Doors).ToArray();
if (walkableMesh.Length > 0){
this.WalkableBVH =
new EmbreeBVH(walkableMesh);
}
}
private void PlotNodes(Vector3[] nodes, int r = 0, int g = 0, int b = 0)
{
Color color = new Color(r, g, b);
for (int i = 0; i < nodes.Length; i++)
{
nodeVisualizer.VisualizeAllToAllNode(node, color);
}
}
public bool CreateGraph(Vector3 StartPoint)
{
if (this.WalkableBVH == null) return false;
Vector3D start = MeshUtils.ConvertToVector3D(StartPoint);
Debug.Log("Converted start of graph: " + start);
var graph_watch = System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch.StartNew();
graph_watch.Stop();
if (this.graph == null)
return false;
else
{
Debug.Log(
"Graph Generated " + graph.
NumNodes().ToString() +
" nodes in " + graph_watch.ElapsedMilliseconds.ToString() +
"ms");
return true;
}
}
}
A collection of vertices and indices representing geometry.
Definition: MeshInfo.cs:50
string name
Name of the mesh.
Definition: MeshInfo.cs:52
Generate a graph of accessible space on a mesh.
Definition: GraphGenerator.cs:45
static Graph GenerateGraph(EmbreeBVH bvh, Vector3D start_point, Vector3D spacing, int max_nodes=-1, float up_step=0.2f, float up_slope=20, float down_step=0.2f, float down_slope=20, int max_step_connections=1, int min_connections=1, int core_count=-1, int[] obstacle_ids=null, int[] walkable_ids=null)
Generate a graph of accessible space with the given settings. If no graph can be generated,...
Definition: GraphGenerator.cs:101
virtual T[] CopyArray()
Copy the unmanaged array pointed to by this object into a managed array.
Definition: PointerHolder.cs:247
A Bounding Volume Hierarchy for the EmbreeRaytracer.
Definition: EmbreeBVH.cs:31
A graph representing connections between points in space.
Definition: Graph.cs:112
CSRInfo CompressToCSR(string cost_type="")
Compress the graph into a CSR representation, and get pointers to it.
Definition: Graph.cs:241
int NumNodes()
Get the number of nodes in this graph.
NodeList getNodes()
Get an array containing the graph's current nodes.
An array of Nodes directly from a graph in unmanaged memory.
Definition: Node.cs:56
Manipulate and load geometry from disk.
Definition: CommonRotations.cs:4
Generate a graph of accessible space from a given start point.
Definition: GraphGenerator.cs:36
Cast rays to determine if and where they intersect geometry.
Definition: EmbreeBVH.cs:7
Standard fundamental data structures for representing space used throughout DHARTAPI.
Definition: Graph.cs:20
A point in space.
Definition: Node.cs:17
Once this script is created, select the Main Camera, which should have your script, drag the empty game object called GraphStart and the Mesh model to the "Mesh Parent" space.
Helper Scripts
- Create a script called
MeshUtils.cs
- Create a script called
TransformUtils.cs
These do not need to be assigned to any object.
The MeshUtils.cs continues from the previous script:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.Rendering;
public static class MeshUtils
{
static public Mesh CombineSubmeshes(Mesh mesh, Matrix4x4 matrix)
{
List<CombineInstance> ci = new List<CombineInstance>();
for (int i = 0; i < mesh.subMeshCount; i++)
{
CombineInstance combine = new CombineInstance();
combine.mesh = mesh;
combine.transform = matrix;
combine.subMeshIndex = i;
ci.Add(combine);
}
Mesh out_mesh = new Mesh();
out_mesh.indexFormat = IndexFormat.UInt32;
out_mesh.CombineMeshes(ci.ToArray(), true, true);
out_mesh.name = mesh.name;
return out_mesh;
}
public static Mesh[] GetMeshesFromParent(GameObject MeshParent)
{
var mesh_renders = MeshParent.GetComponentsInChildren<MeshFilter>();
List<Mesh> out_meshes = new List<Mesh>();
foreach (var filter in mesh_renders)
{
out_meshes.Add(MeshUtils.CombineSubmeshes(filter.mesh, filter.transform.localToWorldMatrix));
}
return out_meshes.ToArray();
}
public static float[] FlattenVerticeArray(Vector3[] inds, bool convert_coord = false)
{
float[] return_array = new float[inds.Length * 3];
for (int i = 0; i < inds.Length; i++)
{
int os = i * 3;
if (convert_coord)
{
return_array[os] = -1 * inds[i].x;
return_array[os + 1] = -1 * inds[i].z;
return_array[os + 2] = inds[i].y;
}
else
{
return_array[os] = inds[i].x;
return_array[os + 1] = inds[i].y;
return_array[os + 2] = inds[i].z;
}
}
return return_array;
}
public static Vector3D ConvertToVector3D(Vector3 PointToConvert,
bool convert_coords =
false)
{
if (convert_coords)
return new Vector3D(-1 * PointToConvert.x, -1 * PointToConvert.z, PointToConvert.y);
else return new Vector3D(PointToConvert.x, PointToConvert.y, PointToConvert.z);
}
}
The TransformUtils.cs has a few helper functions for coordinate conversion as well as datatypes. The code to copy is:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
namespace DHARTUTILS
{
static class TransformUtils
{
public static Vector3[] PointList_Z2Y(Vector3[] nodes_in)
{
Vector3[] nodes = new Vector3[nodes_in.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < nodes.Length; i++)
{
nodes[i].x = nodes_in[i].x;
nodes[i].y = nodes_in[i].z;
nodes[i].z = -1 * nodes_in[i].y;
}
return nodes;
}
public static Vector3[] PointList_R2L(Vector3[] nodes_in)
{
Vector3[] nodes = new Vector3[nodes_in.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < nodes.Length; i++)
{
nodes[i].x = -1 * nodes_in[i].x;
nodes[i].y = nodes_in[i].y;
nodes[i].z = nodes_in[i].z;
}
return nodes;
}
public static List<Vector3D> ToVector3D(Vector3[] nodes_in)
{
List<Vector3D> v3d_nodes = new List<Vector3D>();
for (int i = 0; i < nodes_in.Length; i++)
{
v3d_nodes.Add(nodePos);
}
return v3d_nodes;
}
public static Vector3[] Node_to_Vector(
Node[] nodesList)
{
Vector3[] node_vec = new Vector3[nodesList.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < nodesList.Length; i++)
node_vec[i] = new Vector3(nodesList[i].x, nodesList[i].y, nodesList[i].z);
return node_vec;
}
}
}
- Create an empty game object called
GraphStart
Place this object above the geometry in which you will generate a graph.